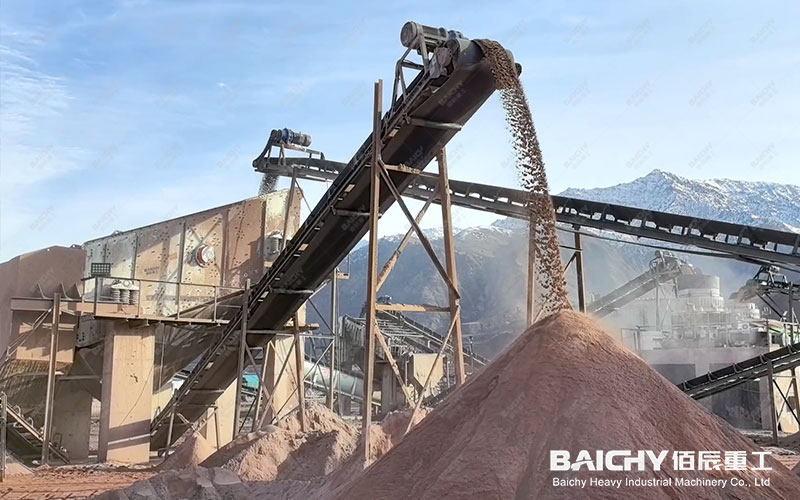
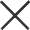
1. Crushing
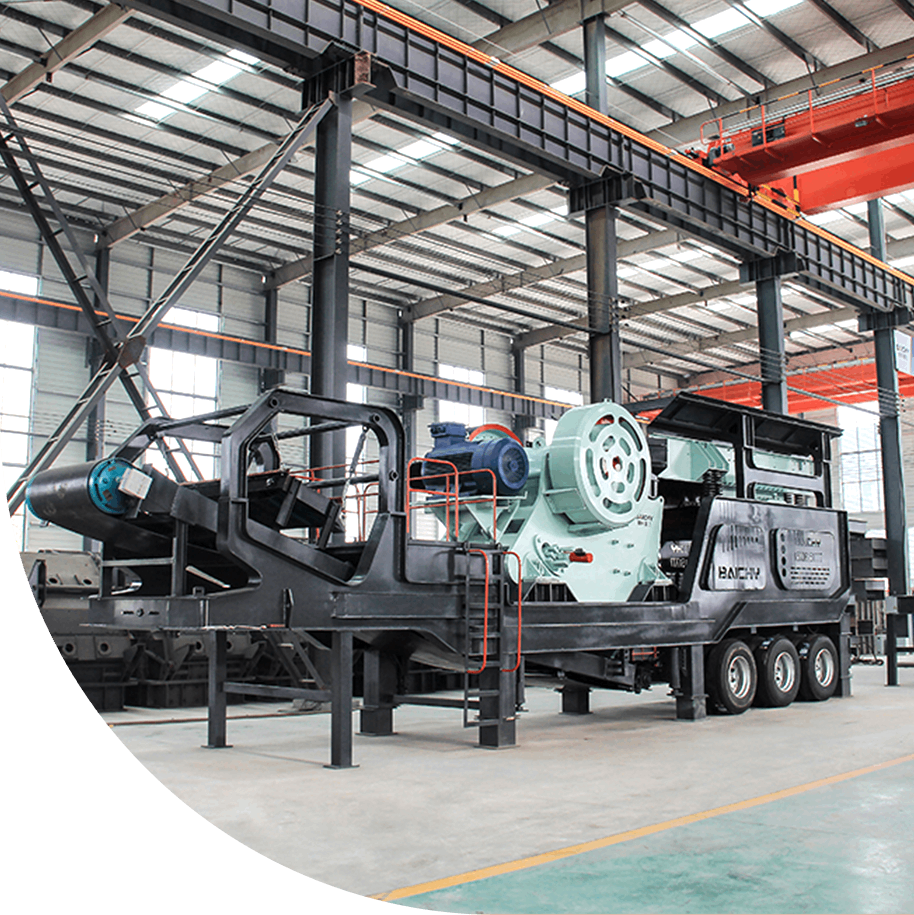
• Preliminary crushing: Use a jaw crusher to crush large pieces of gold ore into smaller particles. The jaw crusher ensures that the ore can smoothly enter the next stage with its high crushing ratio (generally 3-4) and effective crushing capacity.
• Screening: The crushed ore is screened by linear vibrating screens and other equipment, and the ore that does not meet the particle size requirements is returned to the crusher for re-crushing until the required particle size is reached.
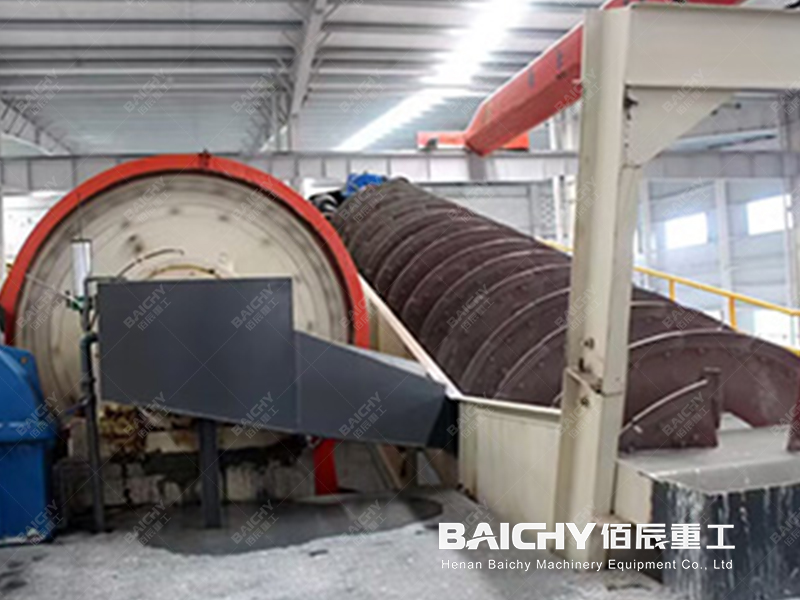
2. Grinding
• Fine grinding: The crushed ore enters the ball mill for fine grinding. The slurry after grinding needs to reach a certain fineness (-200 mesh ore should reach more than 45%) to facilitate subsequent flotation operations.
• Classification: The slurry after grinding is classified by hydrocyclones and other equipment, and the slurry that meets the requirements is sent to the mixing barrel to mix with the reagent.
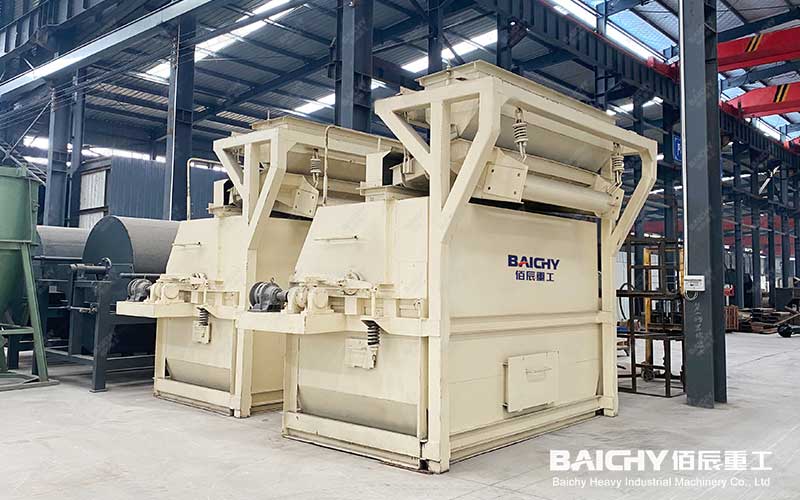
3. Flotation
• Agent mixing: In the mixing barrel, the pulp and flotation reagent are fully mixed to produce a significant difference in floatability between the useful minerals and gangue minerals in the ore.
• Flotation operation: The mixed pulp is sent to the flotation machine, and the useful minerals are floated to the foam layer by the action of bubbles, while the gangue minerals remain in the pulp. Commonly used flotation equipment includes mechanical stirring flotation machines (such as SF type, JJF type, BF type) and aerated stirring flotation machines (such as XCF type, KYF type).
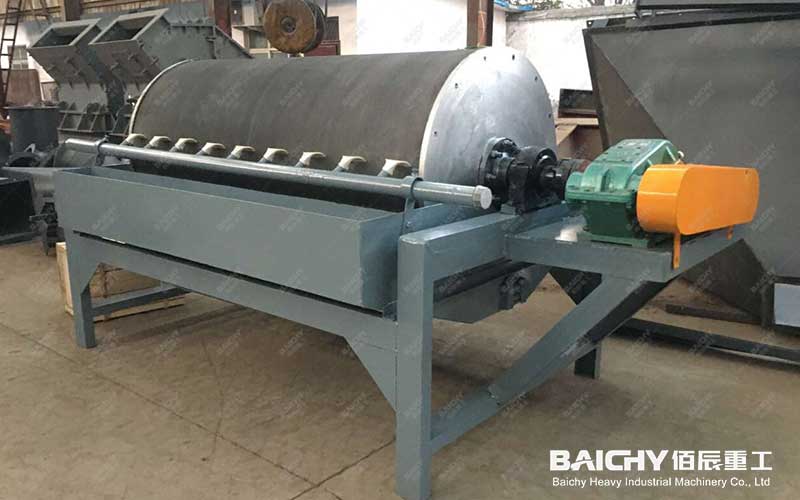
4. Dehydration
• Concentration: The concentrate after flotation is initially concentrated by the concentrator to reduce the moisture content.
• Dehydration: The concentrated concentrate is further dehydrated using equipment such as a filter press or a centrifuge to achieve the dryness required for smelting.
5. Smelting
• The dehydrated concentrate will be sent to the smelter for further processing and purification, and finally the finished gold will be obtained. The smelting process may involve a variety of chemical and physical methods, such as smelting, electrolysis, etc.