Dry ball mill and wet ball mills are two common types of ore grinding equipment, and they differ significantly in many aspects. Here's a detailed comparison of the two devices:
Working principle of ball mill
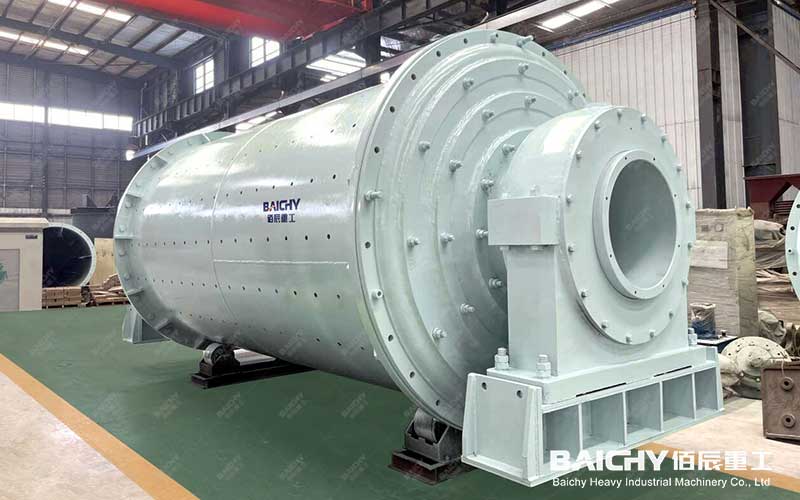
1. Dry ball mill: The material enters the first chamber of the mill evenly and spirally from the feeding device through the feeding hollow shaft. The chamber is equipped with stepped linings or corrugated linings and is equipped with steel balls of different specifications. The centrifugal force generated by the rotation of the ball mill barrel brings the steel balls to a certain height and then falls, thereby crushing and grinding the materials. After the materials are coarsely ground in the first chamber, they enter the second chamber through a single-layer partition board. This chamber is equipped with a flat liner and equipped with steel balls of different specifications to further grind the materials.
2. Wet ball mill: The working principle is roughly the same as that of a dry ball mill, but an appropriate amount of water or anhydrous ethanol needs to be added during the grinding process. There are certain requirements for the grinding concentration. The amount of water is determined by the properties of the material. Qualified materials are discharged out of the cylinder through the discharge part, while unqualified materials are returned to the wet ball mill for re-grinding.
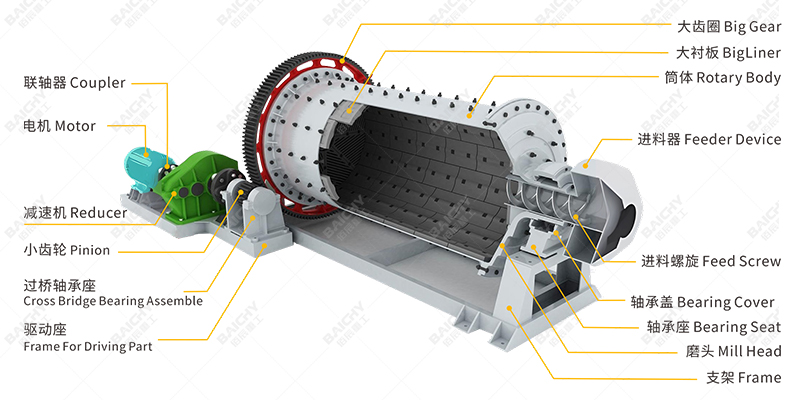
Structural structure of ball mill
1. Dry ball mill: The structure is relatively complex, including the feeding part, the discharging part, the rotating part, the transmission part (reducer, small transmission gear, motor, electronic control), and other main parts. The discharge port is in the shape of a straight cylinder and is equipped with an air induction device, a dust exhaust pipe, and a dust collector, which is also determined by its working principle.
2. Wet ball mill: The structure is relatively simple and also includes a feeding part, a discharging part, a rotary part, a transmission part, and other parts. However, there is no need to add too many auxiliary accessories. The discharge port is trumpet-shaped and has a built-in screw device to facilitate discharge.
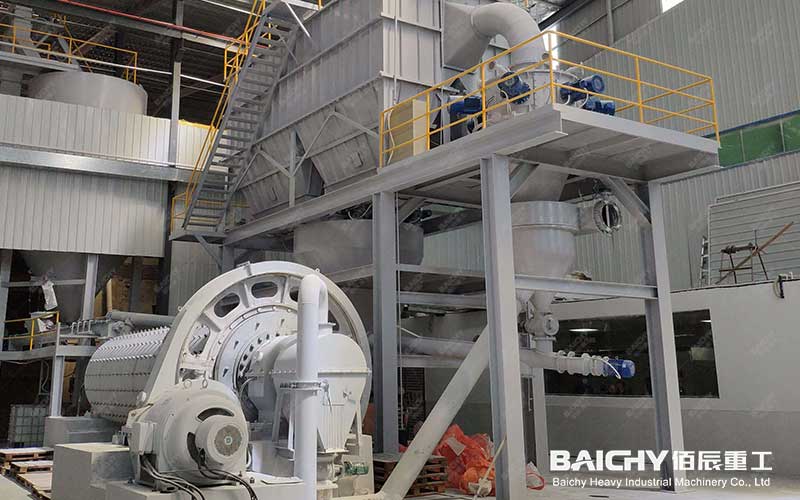

Dry Ball Mill
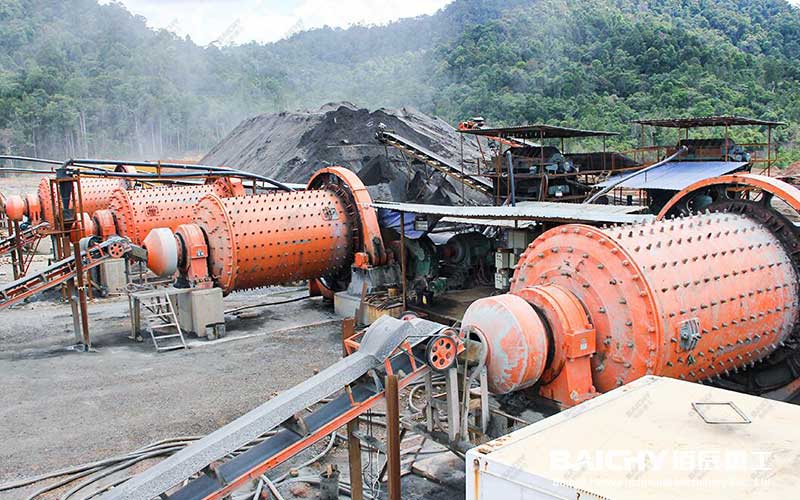

Wet Ball Mill
Application scope of ball mill
1. Dry ball mill: suitable for various metal ores, non-metallic ores, etc., especially materials that react with water, such as cement, marble, and other building stones, or products that require storage and sales in powder form. In addition, if the processing plant is located in an arid area with scarce water resources, a dry ball mill can be used to save water.
2. Wet ball mill: has a wide range of applications and can process various metallic ores and non-metallic ores. Common ones include gold ore, silver ore, copper ore, iron ore, molybdenum ore, phosphate ore, feldspar ore, fluorite ore, etc.. As long as it is ensured that the quality of the final product will not be affected when the material encounters water, a wet ball mill can be used. Ore that needs to be sorted is usually processed by a wet ball mill.
Energy consumption and environmental protection of ball mills
1. Dry ball mill: Although it does not require water resources, due to the influence of the humidity of the ore, a very thin material layer is formed on the surface of the ore and lining plate, so the energy consumption per ton of ore is relatively high. At the same time, since the dry ball mill will generate dust during operation, it needs to be equipped with dust removal equipment.
2. Wet ball mill: Since the addition of liquid as a medium helps prevent dust from flying, it has better environmental performance. At the same time, the energy consumption of wet ball mills is relatively low, and the production investment cost is also small.
Ball mill operation and maintenance
1. Dry ball mill: The structure is relatively simple, and the operation and maintenance are relatively convenient. The equipment operates smoothly and reliably, with small vibration and noise below a certain decibel (such as 85 decibels).
2. Wet ball mill: It also has the characteristics of easy operation and maintenance. However, due to the addition of a liquid medium, the operating status of the liquid system needs to be checked regularly.
There are significant differences between dry ball mills and wet ball mills in terms of working principle, structural structure, scope of application, energy consumption, and environmental protection, as well as operation and maintenance. When selecting, comprehensive considerations should be made based on factors such as material properties, product requirements, working environment, and production costs.
Common problems and solutions for ball mills
1. Motor-related problems, the motor cannot start
Possible reasons: power is not connected; fuse is blown; overcurrent relay is adjusted too small; load is too large; control equipment wiring is wrong.
Solution: Check the switch, fuse and each contact, repair the fault; find out the cause of the fuse burnout and eliminate it, and then match the new fuse according to the specification; appropriately increase the relay current; reduce the load or adjust the feed quantity; correct the wiring error.
2. The speed of the motor is lower than the rated value when it is running with load
Possible reasons: the power supply voltage is too low; one phase of the wound rotor is broken; the load is too large.
Solution: Use a voltmeter and a multimeter to check the power supply voltage at the input end of the motor; use a test lamp, a multimeter, etc. to check the break and eliminate the fault; reduce the load or adjust the feed quantity.
3. The sound of the motor is abnormal when it is running
Possible reasons: the stator and the rotor rub against each other, the bearing runs on the inner circle or outer circle; the motor runs in the absence of phase; the rotor fan blade hits the shell; the bearing is short of oil.
Solution: Replace the shaft, bearing, end cover, and file off the rubbed part of the rotor silicon steel sheet; check the switch and contacts and eliminate the fault; correct the fan blade and tighten the fan blade cover screw; clean the bearing and add new oil (such as 3# molybdenum disulfide lithium grease), and control the filling amount to 65%~70% of the bearing volume.
4. Speed and load problems
The ball mill runs too slowly and the load is heavy
Possible reasons: lack of oil or excessive oil in the coupling.
Solution: Appropriately increase or decrease the hydraulic oil.
5. Bearing problem
The large bearings at both ends make abnormal sounds when the cylinder is running
Possible reasons: the bearing runs on the inner circle or outer circle; the bearing lacks oil; the bearing is damaged.
Solution: Repair the shaft head and bearing seat; add new oil; replace the bearing.
6. Motor deceleration vibration
Possible reasons: the shaft head is bent; the fastening screws are loose; the bearing is damaged.
Solution: Correct or replace the shaft; tighten the screws; replace the damaged bearing.
7. Other common problems
Grounding failure, motor housing is electrified
Possible reasons: the power cord and grounding wire are wrong; the motor winding is damp, the insulation is aged, or the lead wire touches the junction box.
Solution: Correct the wiring; dry the motor winding, replace the wire group if the insulation is aged, and tidy up the grounding wire.
8. The V-belt slips and is difficult to start
Possible reasons: the V-belt is too loose; the space in the ball mill is too large, the material is too little; the material-water ratio is wrong, and the water volume is insufficient.
Solution: Tighten the V-belt; adjust the material amount and add ball stones; open the ball cover and add water.
9. The cylinder rotates with the center of gravity when releasing the slurry
Possible reasons: the brake is aged; the brake is too loose; the ball position is not set before releasing the slurry.
Solution: Replace the brake pads; tighten the brakes; set the ball position according to the operating specifications before releasing the slurry.
10. The ball mouth leaks slurry
Possible reasons: the ball mouth screw is not tightened; the ball mouth seal is aged and damaged; the ball mouth cover is not cleaned before closing, and there are debris on the edge.
Solution: Stop the ball, tighten the screws and then restart the machine; replace the sealing ring; remove the ball cover and clean the edge of the ball mouth before covering it.
11. Reducer oil leakage
Possible reasons: excessive oil filling; damaged seals.
Solution: Release excess oil; replace seals.
12. Ball mill bearing overheating, motor overload
Possible reasons: The lubricating oil brand is inconsistent with the equipment manual or the lubricating oil is deteriorated; too much or too little grease; the lubrication pipeline is blocked so that the lubricating oil does not enter the lubrication point; the bearing or coupling is not installed correctly; the gap between the shaft neck and the bearing is too large or too small, resulting in poor contact; the oil tank is damaged so that the oil cannot flow into the shaft neck or bearing.
Solution: Use the correct brand of lubricating oil and replace the deteriorated lubricating oil; add enough oil as required (generally 1/3~1/2 of the bearing clearance); dredge the lubrication pipeline; correctly install the bearing or coupling; adjust the gap between the shaft neck and the bearing; check and repair the oil tank in time.
13. The ball mill has a dull sound, the ammeter reading drops, and the discharge is small
Possible reasons: too much filling material and large particle size; improper filling of the grinding body or imbalance caused by bin crossover, and unreasonable length of each bin.
Solution: Reduce the filling material and reduce the particle size of the grinding body; adjust the grinding body ratio and the length of each bin.
The ball mill may encounter various problems during use. In order to ensure its normal operation and extend its service life, it is necessary to regularly inspect and maintain the equipment to detect and solve problems in time.