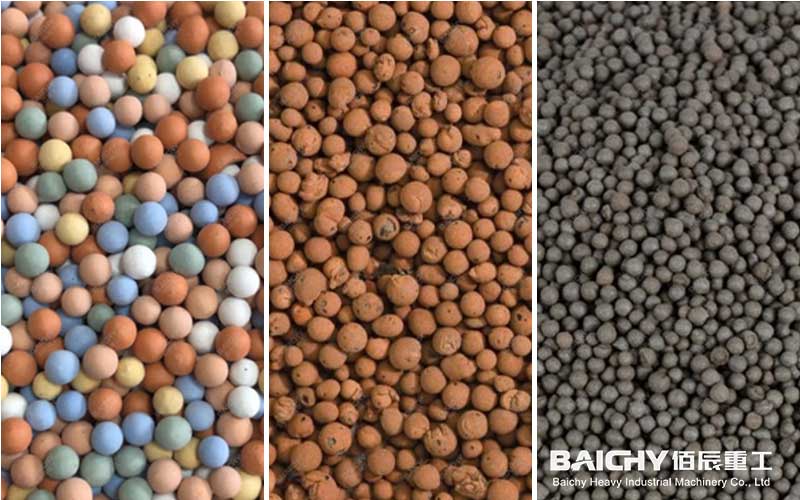
What is ceramsite sand?
Most ceramsite sands are round or oval spheres, but some imitation gravel ceramsites are irregular gravel. Its color varies depending on the raw materials and processes used. Common colors include dark red, ochre red, grayish yellow, etc., while petroleum proppants may appear black, grayish white, blue-gray, etc.
Ceramic sand has multifunctional characteristics such as light weight, high strength, corrosion resistance, frost resistance, earthquake resistance and good insulation. These characteristics make ceramsite sand widely used in many fields.
Compared with other ordinary building materials, what are the advantages of ceramsite sand?
1. The density of ceramsite sand is much lower than that of traditional building materials such as crushed stone and pebbles, which makes it more convenient in transportation and construction, reducing the difficulty and cost of construction. The light weight also allows ceramsite sand to reduce the overall weight in buildings, which helps to reduce the foundation load of buildings.
2. Ceramic sand is fired at high temperature, has high strength and cylinder pressure strength, and can withstand greater pressure without being easily broken. This high-strength property makes ceramsite sand have better durability and stability in building materials
3. Ceramsite sand is porous inside and has good thermal insulation properties. Using ceramsite sand as an insulation material in buildings can effectively reduce energy loss and improve the thermal insulation performance of buildings.
4. Ceramsite sand has low water absorption and better permeability than ordinary concrete. This makes it less likely to absorb water and expand in a humid environment, thus ensuring the stability and durability of the building. Ceramsite sand has excellent fire resistance and strong stability, and can maintain good performance in cold areas without being easy to break.
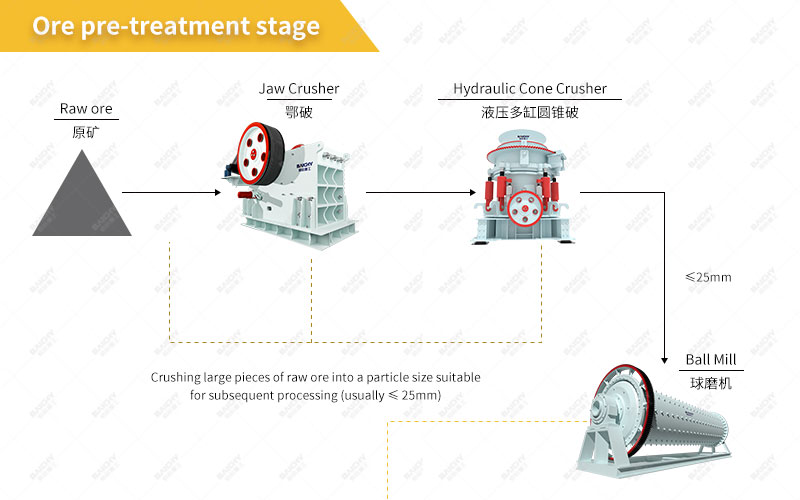
How to produce ceramsite sand?
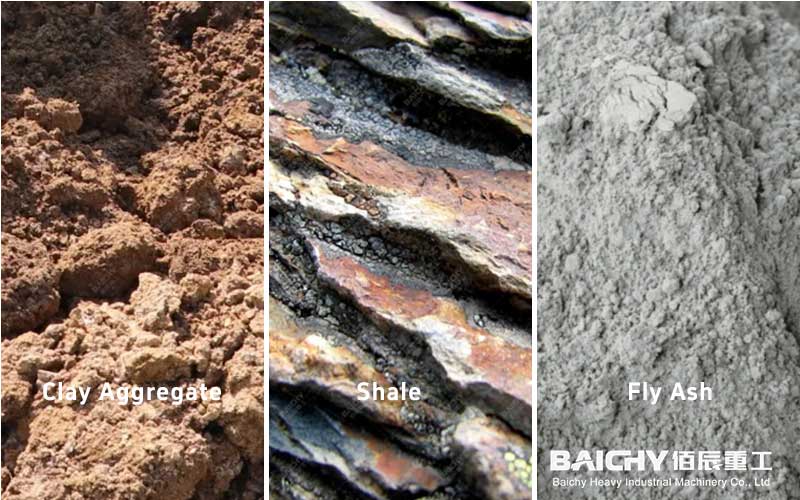

1. Raw material preparation and processing
Raw material selection: Select suitable clay, mudstone, coal gangue, slate, shale or industrial solid waste as the main raw materials.
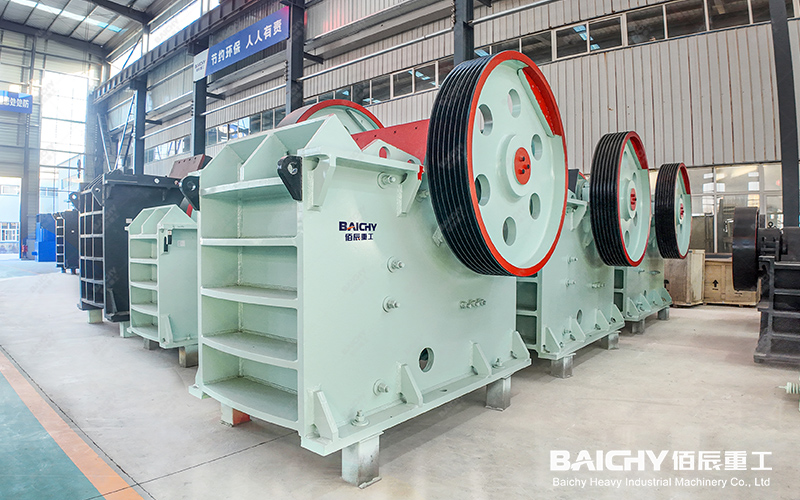
Crushing and screening: The mined raw materials are crushed, usually using a jaw crusher for coarse crushing, and then a cone crusher for secondary crushing, and the particle size is controlled within a certain range (such as less than 8 mm). The crushed raw materials need to be screened to remove particles that do not meet the requirements.
2. Batching and mixing
Batching: According to production requirements, different types of raw materials are batched in a certain proportion to ensure that the chemical composition and physical properties of the product meet the requirements.
Mixing: Mix the batched raw materials to make them evenly distributed to prepare for the subsequent ball making and calcining process.
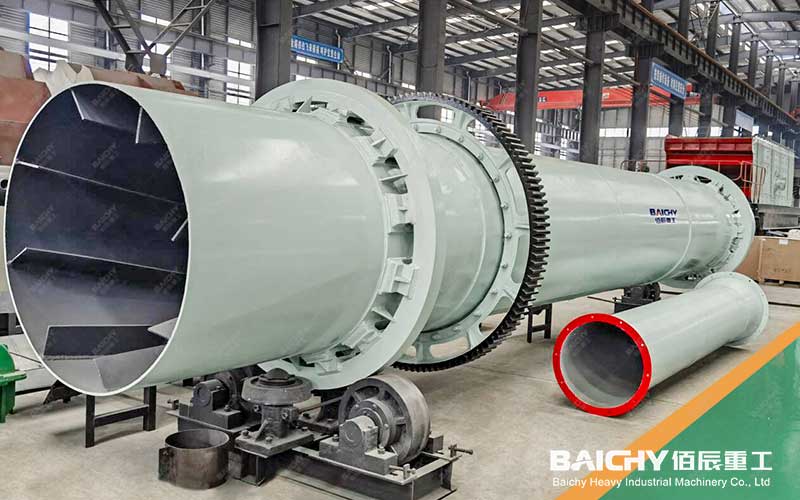

3. Ball making and drying
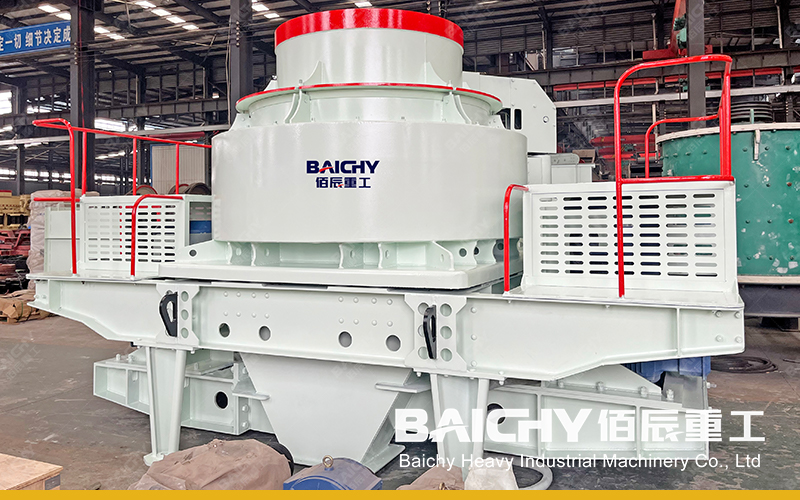
Ball making: The mixed raw materials are sent to the ball making machine, and an appropriate amount of water is added for mixing. Through the rotation and extrusion of the ball making machine, the raw materials are made into balls with a certain strength and shape.
Drying: The prepared balls are dried to remove the moisture in them to prevent cracks or ruptures during the subsequent calcining process.
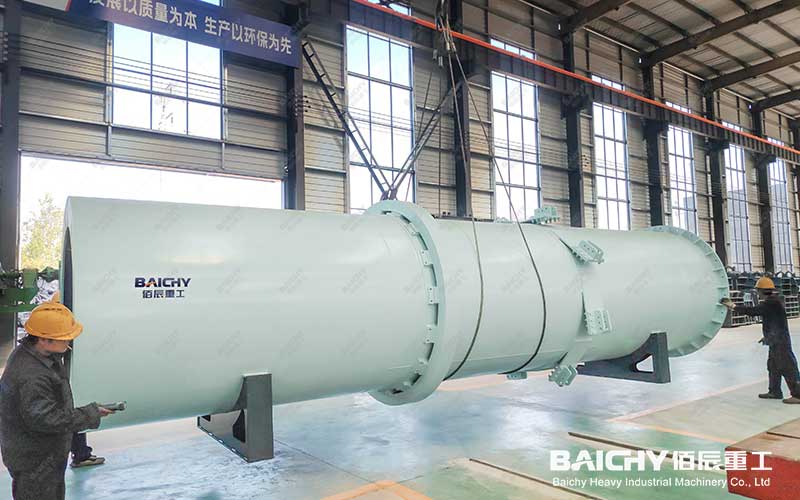

4. Calcination and cooling
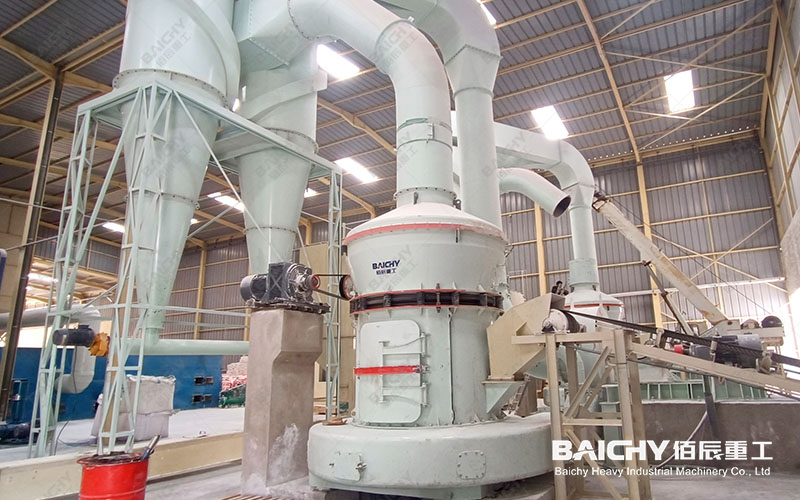
Calcination: The dried balls are sent to the rotary kiln for calcination. In the rotary kiln, the balls roll with the rotation of the kiln body, and the fuel (such as coal powder) in the kiln is burned to produce a high temperature environment. The pellets undergo physical and chemical changes at high temperatures to form ceramsite sand with a certain strength and density.
Cooling: The calcined ceramsite sand needs to be cooled to reduce its temperature and improve its stability. Usually a rotary cooler is used for cooling, and the cooled ceramsite sand can be directly screened and graded.
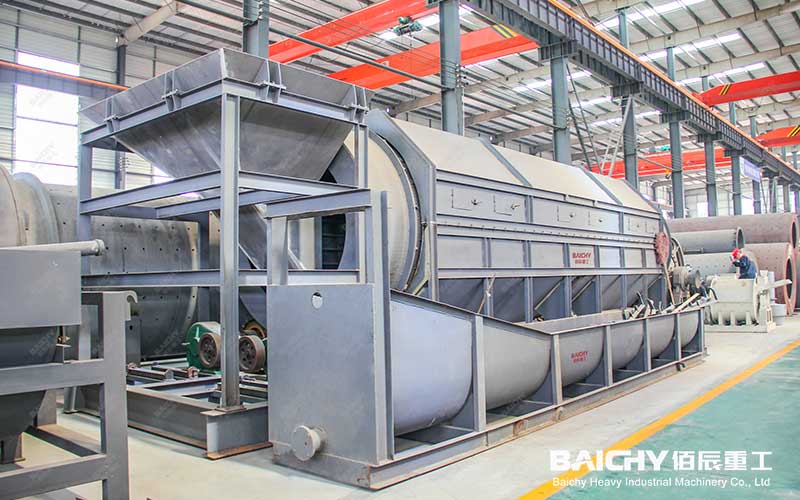

5. Screening and grading
Screening: The cooled ceramsite sand is screened to remove impurities and particles that do not meet the requirements.
Grading: Grading is performed according to the particle size of the ceramsite sand to meet the needs and application scenarios of different customers.
6. Quality control and testing
In the production process of ceramsite sand, strict quality control and testing are required for each link. This includes testing and analyzing the chemical composition, physical properties, particle size distribution and other indicators of raw materials, semi-finished products and finished products to ensure that the product quality meets the relevant standards and customer needs.
The production process of ceramsite sand is a complex and sophisticated system engineering, which requires strict control of process parameters and quality indicators in each link. Through reasonable raw material selection, batching and mixing, ball making and drying, calcination and cooling, screening and grading, as well as quality control and testing, expanded clay sand products with stable quality and excellent performance can be produced.